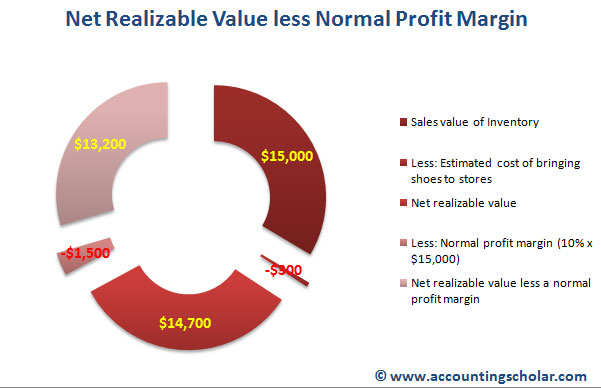
In brief, LCM allowed accountants to measure inventories at the lower of historical cost or market value, where market value could mean replacement cost, net realizable value (NRV), or NRV less a normal profit margin. Accounting conservatism is a principle that requires company accounts to be prepared with caution and high degrees of verification. These bookkeeping guidelines must be followed before a company can make a legal claim to any profit.
Formula and Calculation of Net Realizable Value
When it comes to inventory valuation, you may have come across the terms ‘Lower of Cost or Market’ (LCM) and ‘Lower of Cost or Net Realizable Value’ (LCNRV). While they seem similar, there are nuanced differences between the two methods, especially post the FASB update in 2015 replacing the LCM with LCNRV in the GAAP framework. As part of this filing, Volkswagen disclosed the nature of the calculation of its inventory. In compliance with prevailing accounting regulation, Volkswagen considered net realizable value when determining its inventory value. US GAAP, although broadly consistent with IFRS, prohibits the reversal of write-downs.
Retail method cost is reviewed regularly under IAS 2; not under US GAAP
In a constantly evolving economic landscape, NRV calculations can be significantly impacted. Companies may find that as the market’s preferences evolve, factors such as substitute products and shifting fiscal policies, including taxes, can markedly alter the Net Realizable Value (NRV) of their assets. Consider the implications of inflation, for example, which can erode the purchasing power of customers, leading to reduced demand and lower expected selling prices for non-essentials or more expensive options when compared to substitute products. Conversely, during periods of economic growth, increased consumer spending can elevate these prices.
What are Net Tangible Assets: Importance, Formula & Example
Under IFRS, inventories may be measured and carried on the balance sheet at a lower cost and net realizable value. US GAAP, on the other hand, specifies the lower cost or market to value inventories. Market value, for this purpose, is defined as the current replacement cost subject to upper and lower limits. You need to add straps and metal accessories to complete the product for sale. Net realizable value can also refer to the aggregate total of the ending balances in the trade accounts receivable account and the offsetting allowance for doubtful accounts.
Thus, the figure reported in the asset section of the balance sheet is lower than the total amount of receivables held by the company. Additional information disclosed by Dell indicates that the company actually held $4.843 billion in accounts receivable but—at the date of the balance sheet—$112 million of these accounts were anticipated to be uncollectible. earned income and earned income tax credit eitc tables Thus, the amount of cash that is estimated to be received is the reported $4.731 billion balance ($4.843 billion total less $112 million expected to be uncollectible). Just determining whether the $112 million in uncollectible accounts is a relatively high or low figure is quite significant in evaluating the efficiency of Dell’s current operations.
What can Net Realizable Value tell you about your business?
In practice, for an acquired business this often requires rapid realignment to its new parent’s group methodologies and systems. In some cases, NRV of an item of inventory, which has been written down in one period, may subsequently increase. In such circumstances, IAS 2 requires the increase in value (i.e. the reversal), capped at the original cost, to be recognized.
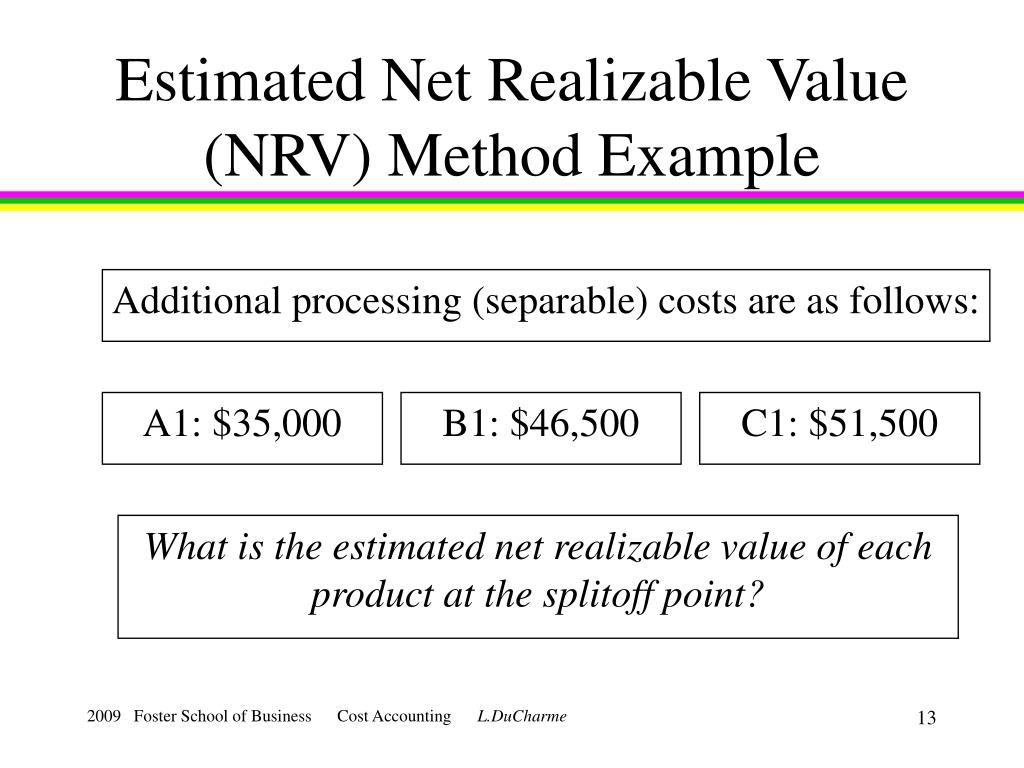
Under IAS 2, inventory may include intangible assets that are produced for resale – e.g. software. Unlike US GAAP, inventories are generally measured at the lower of cost and NRV3 under IAS 2, regardless of the costing technique or cost formula used. The International Accounting Standards Board (IASB® Board) eliminated the use of LIFO because of its lack of representational faithfulness of inventory flows. Fortunately, calculating net realizable value is relatively straightforward. This means that you do not need to use a net realizable value calculator in order to gain access to this vital information.
Within market method accounting, NRV is only used as an approximation of market value when the market value of inventory is unknown. Jami Gong is a Chartered Professional Account and Financial System Consultant. She holds a Masters Degree in Professional Accounting from the University of New South Wales. Her areas of expertise include accounting system and enterprise resource planning implementations, as well as accounting business process improvement and workflow design. Jami has collaborated with clients large and small in the technology, financial, and post-secondary fields.
- Under IFRS, inventories may be measured and carried on the balance sheet at a lower cost and net realizable value.
- GAAP, the figure that is presented on a balance sheet for accounts receivable is its net realizable value—the amount of cash the company estimates will be collected over time from these accounts.
- The financial impact of signing a bank loan or the payment of a salary can be described to the penny except in unusual situations.
- Unlike US GAAP, inventories are generally measured at the lower of cost and NRV3 under IAS 2, regardless of the costing technique or cost formula used.
- This is especially true during inflationary periods when the Federal Reserve is interested in raising rates.
- There is an ongoing need to examine the value of inventory to see if its recorded cost should be reduced, due to the negative impacts of such factors as damage, spoilage, obsolescence, and reduced demand from customers.
Under IAS 2, the cost of inventories measured using the retail method is reviewed regularly, in our view at least at each reporting date, to determine that it approximates cost in light of current conditions. The percentage of gross profit margin is revised, as necessary, to reflect markdowns of the selling price of inventory. Other times NRV is used by accountants to make sure an asset’s value isn’t overstated on the balance sheet.
The differences around costs and measurement between IFRS Standards and US GAAP can be difficult for companies to tackle as they switch between the two standards or conform acquired businesses to group costing policies. This is because changing inventory costing methodologies often requires systems and process changes. These GAAP differences can also affect the composition of costs of sales and performance measures such as gross margin.
Unlike IAS 2, US GAAP allows use of different cost formulas for inventory, despite having similar nature and use to the company. Therefore, each company in a group can categorize its inventory and use the cost formula best suited to it. Items of property plant and equipment that a company holds for rental to others and then routinely sells in the ordinary course of its activities are reclassified to inventory when they cease to be rented and become held for sale. Most businesses rely on cash flow they have yet to receive from customers who have purchased their goods and… Discounted cash flow (DCF) is a valuation method used to estimate a company’s or investment’s intrinsic value…
